Introduction
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, builds 3D objects layer by layer from various materials, each method differing in precision, material options, and costs. In contrast, CNC machining, a subtractive manufacturing process, carves parts from solid blocks using rotating tools. This blog will delve into a detailed comparison of 3D printing and CNC machining, exploring their pros, cons, and alternative applications.
3D Printing Definition and Comparison to CNC Machining
3D printing involves creating objects from virtual models by slicing them into layers and sequentially printing each layer. It utilizes various materials like polymers, resins, and powders, requiring CAD software for design, slicers to convert designs into machine instructions, and specific 3D printer setups.
Commercially viable 3D printing systems emerged in the late 1980s and have since expanded in methods and materials. Compared to CNC machining, 3D printing offers advantages in aesthetics, material efficiency, and the ability to produce complex parts without manual intervention.
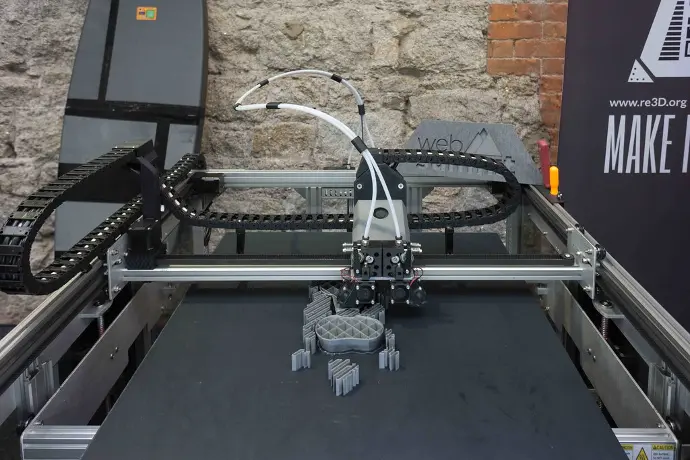
Pros and Cons of 3D Printing
Pros
3D printing produces net shape parts rapidly
3D printing is generally more cost-effective for creating complex net shapes compared to other methods. It requires minimal setup and operational intervention
Office-friendly 3D printers requiring modest setup and maintenance skills are becoming more prevalent. They are increasingly capable of meeting a wide range of manufacturing needs
Cons
3D printing processes vary in strength relative to the materials used
While 3D printing can achieve good dimensional accuracy, achieving high precision can be challenging.
Surface finish in 3D printing can be affected by process mechanics, resulting in stepped surfaces and visual imperfections, especially in Z-resolution.
CNC Machining Definition and Comparison to 3D Printing
CNC machining is an automated manufacturing process that utilizes pre-programmed software and codes to direct the movements of machine tools. This technology employs various sophisticated machinery such as lathes, mills, and grinders to cut, create, and shape parts with accuracy and precision. The first CNC machine was developed by James Parson in 1949, initially focusing on producing helicopter and aircraft blades. In 1958, Richard Kegg and MIT collaborated to create the first CNC milling machine. While CNC machining requires complex setup and is costly, it is preferred over 3D printing for parts needing durability, strength, smooth surfaces, and high precision.

Get Your Free Quote Today
Don't wait any longer on your project!
Pros and Cons of CNC Machining
Pros
CNC machining preserves the full properties of engineering materials without disruption
CNC parts typically achieve higher precision due to the closer tolerances that CNC machines can maintain
Cons
CNC machining often involves the fabrication of mounting tools, which adds complexity to the process
CNC machining removes excess material, generating waste during cutting
3D Printing vs. CNC Machining: Lead Cost and Speed Comparison
CNC machining is more costly than 3D printing due to high setup and programming expenses, typically five to ten times higher. However, CNC allows for cheaper adjustments in iterative prototyping compared to 3D printing, where each print costs the same regardless of changes.
Preparing for 3D printing is quick, with most prints finishing within hours. In contrast, CNC machining requires skilled planning for tool selection and path creation.
While 3D printing is advantageous for cost and time in part production, CNC machining ensures precision akin to mass production standards when high part accuracy is essential.
3D Printing vs. CNC Machining: Volume Comparison
CNC machining can achieve cost-effectiveness by distributing setup efforts across multiple parts, unlike 3D printing where each part incurs the same material and machine costs regardless of volume.
3D Printing vs. CNC Machining: Materials Comparison
CNC machining offers broad material flexibility, accommodating various engineering materials including pre-hardened tool steels through spark-erosion methods. It preserves the original material properties without significant alteration during machining.
In contrast, 3D printing is limited by specific printing processes, which restrict the material choices and may result in printed parts with compromised properties like anisotropic grain, porosity, weak bonding between layers, and the use of non-engineering materials for printability.
Summary
This article presented a comparison of 3D printing to CNC machining, explained what they are, and discussed their different attributes. To learn more about 3D printing and CNC machining, contact a Accurate Machine representative.
Accurate Machine Products provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities, including CNC Machining and other value-added services for all of your prototyping and production needs. Visit our website to learn more or to request a free, no-obligation quote